Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +800 items for all kinds of car, main suitable
for AMERICA & EUROPE market.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 5pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
5. Develope new items: FREE
|
Brand Name |
KOWA DRIVE SHAFT |
|
Item name |
OEM |
|
Car maker |
For all japanese/korean/european/american car |
|
Moq |
5pcs |
|
Guarantee |
12 months |
|
sample |
Available if have stock |
|
Price |
Send inquiry to get lastest price |
|
BOX/QTY |
1PCS/Bag 4PCS /CTNS |
For some items, we have stock, small order (+3000USD) is welcome.
The following items are some of drive shafts, If you need more information, pls contact us for ASAP.
| For Japanese Car | |||
| for TOYOTA | for TOYOTA | ||
| 43420-57170 | 43420-57180 | 43410-0W081 | 43420-0W080 |
| 43410-57120 | 43420-57190 | 43410-0W091 | 43420-0W090 |
| 43410-57130 | 43420-57120 | 43410-0W100 | 43420-0W110 |
| 43410-57150 | 43420-02B10 | 43410-0W110 | 43420-0W160 |
| 43410-06221 | 43420-02B11 | 43410-0W140 | 43420-32161 |
| 43410-06231 | 43420-02B60 | 43410-0W150 | 43420-33250 |
| 43410-06460 | 43420-02B61 | 43410-0W180 | 43420-33280 |
| 43410-06570 | 43420-02B62 | 43410-12410 | 43420-48090 |
| 43410-06580 | 43420-06221 | 43410-33280 | 43420-48091 |
| 43410-066-90 | 43420-06231 | 43410-33290 | 43430OK571 |
| 43410-06750 | 43420-06460 | 43410-33330 | 66-5245 |
| 43410-06780 | 43420-06490 | 43410-48070 | 66-5247 |
| 43410-06A40 | 43420-06500 | 43410-48071 | 43420-57150 |
| 43410-06A50 | 43420- 0571 0 | 43410-0W061 | 43420-0W061 |
| 43410-07070 | 43420-06610 | 43410-0W071 | 43420-0W071 |
| for Acura | for LEXUS | ||
| 44305STKA00 | 66-4198 | 43410-06200 | 43410-06480 |
| 44305STKA01 | 66-4261 | 43410-06450 | 43410-06560 |
| 44305SZPA00 | 66-4262 | 66-5265 | |
| 44306STKA00 | 66-4270 | for MITSUBISHI | |
| 44306STKA01 | 66-4271 | 3815A309 | 3815A310 |
| 44306SZPA00 | |||
| for Honda | for MAZDA | ||
| 44571S1571 | 44306S3VA61 | 5L8Z3A428AB | GG052550XD |
| 44011S1571 | 44306S3VA62 | 5L8Z3A428DA | GG052560XE |
| 44305S2HN50 | 44306S9VA51 | 66-2090 | GG362550XA |
| 44305SCVA50 | 44306S9VA71 | 6L8Z3A428A | YL8Z3A427AA |
| 44305SCVA51 | 44306SCVA50 | 9L8Z3A427B | YL8Z3A427BA |
| 44305SCVA90 | 44306SCVA51 | GG032550XD | YL8Z3A428AA |
| 44305SCVA91 | 44306SCVA90 | GG042550XD | YL8Z3A428BA |
| 44305STXA02 | 44306SCVA91 | GG042560XG | ZC32550XA |
| 44305SZAA01 | 44306STXA02 | for Nissan | |
| 44306S2H951 | 44306SZAA01 | 39101-1HS0A | 39100-1HS0A |
| 44306SZAA11 | 44306SZAA01RM | 39101-1HS0B | 39100-1HS0B |
| 44306SZAA12 | 66-4213 | ||
| 66-4214 | |||
| for Europe Car | |||
| for VOLKSWAGEN | for VOLKSWAGEN | ||
| 4885712AD | 7B0407271B | 7E0407271G | 7LA407272C |
| 4885713AF | 7B0407272 | 7E0407271P | 7LA4 0571 2CX |
| 4881214AE | 7B0407272E | 7LA407271E | |
| 7B0407271A | |||
| for America Car | |||
| for CHRYSLER | for MERCURY | ||
| 4593447AA | 557180AD | 4F1Z3B437AA | GG322560X |
| 4641855AA | 52114390AB | 5L8Z3A428DB | GG362560XA |
| 4641855AC | 5273546AC | 66-2249 | YL8Z3A427CA |
| 4641856AA | 66-3108 | 9L8Z3A427C | YL8Z3A427DA |
| 4641856AC | 66-3109 | 9L8Z3A427D | YL8Z3A427EA |
| 4882517 | 66-3130 | GG062550XD | YL8Z3A427FA |
| 4882518 | 66-3131 | GG062560XE | YL8Z3A428CA |
| 4882519 | 66-3234 | GG312560X | ZZDA2560X |
| 4882520 | 66-3518 | ZZDA2560XC | ZZDA2560XA |
| 557130AB | 66-3520 | for RAM | |
| 66-3552 | 66-3522 | 4885713AD | 55719AB |
| 66-3553 | 66-3551 | 4881214AD | 66-3404 |
| 66-3554 | 66-3639 | 55719AA | 66-3740 |
| 68193908AB | 66-3641 | 68571398AA | |
| for FORD | for DODGE | ||
| 1F0571400 | E6DZ3V428AARM | 4593449AA | 7B0407272A |
| 1F0571410 | E8DZ3V427AARM | 4641855AE | 7B0407272B |
| 1F2Z3B436AA | E8DZ3V428AARM | 4641855EE | 7B0407272C |
| 2F1Z3A428CA | E90Y3V427AARM | 4641856AD | R4881214AE |
| 2M5Z3B437CA | E90Y3V428AARM | 4641856AF | RL189279AA |
| 4F1Z3B437BA | F0DZ3V427AARM | 4885710AC | 557180AG |
| 5M6Z3A428AA | F0DZ3V428AARM | 4885710AE | 5170822AA |
| 5S4Z3B437AA | F21Z3B437A | 4885710AF | 52114390AA |
| 66-2005 | F21Z3B437B | 4885710AG | 5273546AD |
| 66-2008 | F2DZ3B436A | 4885711AC | 5273546AE |
| 66-2571 | F2DZ3B436B | 4885711AD | 5273546AF |
| 66-2084 | F2DZ3B437A | 4885712AC | 5273558AB |
| 66-2086 | F2DZ3B437B | 4885712AE | 5273558AD |
| 66-2095 | F4DZ3B437A | 4885712AG | 5273558AE |
| 66-2101 | F57Z3B436BA | 4885712AH | 5273558AF |
| 66-2143 | F57Z3B437BA | 4885713AC | 4881214AC |
| 6S4Z3B437BA | F5DZ3A427BA | 4885713AG | 4881214AF |
| 8S4Z3B437A | F5DZ3A428AS | 4885713AI | 4881214AG |
| 9L8Z3A427A | F5DZ3B426D | 4885713AJ | 557130AA |
| E6DZ3V427AARM | F5DZ3B436D | 5273558AG | 557180AE |
| YF1Z3A428RS | F5DZ3B437B | 66-3382 | 557180AF |
| YL8Z3A428DA | F5TZ3B436A | 66-3511 | 66-3514 |
| YS4Z3B437BB | GG032560XG | 66-3759 | 66-3564 |
| YS4Z3B437CB | GG362550X | ||
| YF1Z3A427L | |||
| for CHEVROLET | for JEEP | ||
| 257191 | 26062613 | 4578885AA | 5215710AA |
| 22791460 | 4578885AB | 5215711AB | |
| 26011961 | 4578885AC | 5215711AB | |
| 26571730 | 2657189 | 4720380 | 5273438AC |
| 2657165 | 66-1401 | 4720381 | 5273438AD |
| 26058932 | 66-1438 | 5012456AB | 5273438AE |
| 26065719 | 88982496 | 5012457AB | 5273438AG |
| for HUMMER | 5066571AA | 66-3220 | |
| 1571204 | 595716 | 557120AB | 66-3221 |
| 15886012 | 66-1417 | 557120AC | 66-3298 |
| for CADILLAC | 557120AD | 66-3352 | |
| 88957151 | 66-1416 | 557120AE | 66-3417 |
| 66-1009 | 66-1430 | 5189278AA | 66-3418 |
| 66-1415 | 88957150 | 5189279AA | 66-3419 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in speed and torque during operation by employing specific mechanisms and configurations. These mechanisms allow the drive shafts to accommodate the changing demands of power transmission while maintaining smooth and efficient operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque:
1. Flexible Couplings:
Drive shafts often incorporate flexible couplings, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to handle variations in speed and torque. These couplings provide flexibility and allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned. U-joints consist of two yokes connected by a cross-shaped bearing, allowing for angular movement between the drive shaft sections. This flexibility accommodates variations in speed and torque and compensates for misalignment. CV joints, which are commonly used in automotive drive shafts, maintain a constant velocity of rotation while accommodating changing operating angles. These flexible couplings enable smooth power transmission and reduce vibrations and wear caused by speed and torque variations.
2. Slip Joints:
In some drive shaft designs, slip joints are incorporated to handle variations in length and accommodate changes in distance between the driving and driven components. A slip joint consists of an inner and outer tubular section with splines or a telescoping mechanism. As the drive shaft experiences changes in length due to suspension movement or other factors, the slip joint allows the shaft to extend or compress without affecting the power transmission. By allowing axial movement, slip joints help prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft during variations in speed and torque, ensuring smooth operation.
3. Balancing:
Drive shafts undergo balancing procedures to optimize their performance and minimize vibrations caused by speed and torque variations. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, which not only affect the comfort of vehicle occupants but also increase wear and tear on the shaft and its associated components. Balancing involves redistributing mass along the drive shaft to achieve even weight distribution, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance. Dynamic balancing, which typically involves adding or removing small weights, ensures that the drive shaft operates smoothly even under varying speeds and torque loads.
4. Material Selection and Design:
The selection of materials and the design of drive shafts play a crucial role in handling variations in speed and torque. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their ability to withstand the forces and stresses associated with varying operating conditions. The diameter and wall thickness of the drive shaft are also carefully determined to ensure sufficient strength and stiffness. Additionally, the design incorporates considerations for factors such as critical speed, torsional rigidity, and resonance avoidance, which help maintain stability and performance during speed and torque variations.
5. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for drive shafts to handle variations in speed and torque. Lubricating the joints, such as U-joints or CV joints, reduces friction and heat generated during operation, ensuring smooth movement and minimizing wear. Adequate lubrication also helps prevent the binding of components, allowing the drive shaft to accommodate speed and torque variations more effectively. Regular lubrication maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the drive shaft.
6. System Monitoring:
Monitoring the performance of the drive shaft system is important to identify any issues related to variations in speed and torque. Unusual vibrations, noises, or changes in power transmission can indicate potential problems with the drive shaft. Regular inspections and maintenance checks allow for the early detection and resolution of issues, helping to prevent further damage and ensure the drive shaft continues to handle speed and torque variations effectively.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation through the use of flexible couplings, slip joints, balancing procedures, appropriate material selection and design, lubrication, and system monitoring. These mechanisms and practices allow the drive shaft to accommodate misalignment, changes in length, and variations in power demands, ensuring efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reduced wear and tear in various applications.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-04-30
China Hot selling Auto Parts Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG Sunny Teana Navara Pickup Car Accessories CV Axle Shaft
Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +800 items for all kinds of car, main suitable
for AMERICA & EUROPE market.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 5pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
5. Develope new items: FREE
|
Brand Name |
KOWA DRIVE SHAFT |
|
Item name |
OEM |
|
Car maker |
For all japanese/korean/european/american car |
|
Moq |
5pcs |
|
Guarantee |
12 months |
|
sample |
Available if have stock |
|
Price |
Send inquiry to get lastest price |
|
BOX/QTY |
1PCS/Bag 4PCS /CTNS |
For some items, we have stock, small order (+3000USD) is welcome.
The following items are some of drive shafts, If you need more information, pls contact us for ASAP.
| For Japanese Car | |||
| for TOYOTA | for TOYOTA | ||
| 43420-57170 | 43420-57180 | 43410-0W081 | 43420-0W080 |
| 43410-57120 | 43420-57190 | 43410-0W091 | 43420-0W090 |
| 43410-57130 | 43420-57120 | 43410-0W100 | 43420-0W110 |
| 43410-57150 | 43420-02B10 | 43410-0W110 | 43420-0W160 |
| 43410-06221 | 43420-02B11 | 43410-0W140 | 43420-32161 |
| 43410-06231 | 43420-02B60 | 43410-0W150 | 43420-33250 |
| 43410-06460 | 43420-02B61 | 43410-0W180 | 43420-33280 |
| 43410-06570 | 43420-02B62 | 43410-12410 | 43420-48090 |
| 43410-06580 | 43420-06221 | 43410-33280 | 43420-48091 |
| 43410-066-90 | 43420-06231 | 43410-33290 | 43430OK571 |
| 43410-06750 | 43420-06460 | 43410-33330 | 66-5245 |
| 43410-06780 | 43420-06490 | 43410-48070 | 66-5247 |
| 43410-06A40 | 43420-06500 | 43410-48071 | 43420-57150 |
| 43410-06A50 | 43420- 0571 0 | 43410-0W061 | 43420-0W061 |
| 43410-07070 | 43420-06610 | 43410-0W071 | 43420-0W071 |
| for Acura | for LEXUS | ||
| 44305STKA00 | 66-4198 | 43410-06200 | 43410-06480 |
| 44305STKA01 | 66-4261 | 43410-06450 | 43410-06560 |
| 44305SZPA00 | 66-4262 | 66-5265 | |
| 44306STKA00 | 66-4270 | for MITSUBISHI | |
| 44306STKA01 | 66-4271 | 3815A309 | 3815A310 |
| 44306SZPA00 | |||
| for Honda | for MAZDA | ||
| 44571S1571 | 44306S3VA61 | 5L8Z3A428AB | GG052550XD |
| 44011S1571 | 44306S3VA62 | 5L8Z3A428DA | GG052560XE |
| 44305S2HN50 | 44306S9VA51 | 66-2090 | GG362550XA |
| 44305SCVA50 | 44306S9VA71 | 6L8Z3A428A | YL8Z3A427AA |
| 44305SCVA51 | 44306SCVA50 | 9L8Z3A427B | YL8Z3A427BA |
| 44305SCVA90 | 44306SCVA51 | GG032550XD | YL8Z3A428AA |
| 44305SCVA91 | 44306SCVA90 | GG042550XD | YL8Z3A428BA |
| 44305STXA02 | 44306SCVA91 | GG042560XG | ZC32550XA |
| 44305SZAA01 | 44306STXA02 | for Nissan | |
| 44306S2H951 | 44306SZAA01 | 39101-1HS0A | 39100-1HS0A |
| 44306SZAA11 | 44306SZAA01RM | 39101-1HS0B | 39100-1HS0B |
| 44306SZAA12 | 66-4213 | ||
| 66-4214 | |||
| for Europe Car | |||
| for VOLKSWAGEN | for VOLKSWAGEN | ||
| 4885712AD | 7B0407271B | 7E0407271G | 7LA407272C |
| 4885713AF | 7B0407272 | 7E0407271P | 7LA4 0571 2CX |
| 4881214AE | 7B0407272E | 7LA407271E | |
| 7B0407271A | |||
| for America Car | |||
| for CHRYSLER | for MERCURY | ||
| 4593447AA | 557180AD | 4F1Z3B437AA | GG322560X |
| 4641855AA | 52114390AB | 5L8Z3A428DB | GG362560XA |
| 4641855AC | 5273546AC | 66-2249 | YL8Z3A427CA |
| 4641856AA | 66-3108 | 9L8Z3A427C | YL8Z3A427DA |
| 4641856AC | 66-3109 | 9L8Z3A427D | YL8Z3A427EA |
| 4882517 | 66-3130 | GG062550XD | YL8Z3A427FA |
| 4882518 | 66-3131 | GG062560XE | YL8Z3A428CA |
| 4882519 | 66-3234 | GG312560X | ZZDA2560X |
| 4882520 | 66-3518 | ZZDA2560XC | ZZDA2560XA |
| 557130AB | 66-3520 | for RAM | |
| 66-3552 | 66-3522 | 4885713AD | 55719AB |
| 66-3553 | 66-3551 | 4881214AD | 66-3404 |
| 66-3554 | 66-3639 | 55719AA | 66-3740 |
| 68193908AB | 66-3641 | 68571398AA | |
| for FORD | for DODGE | ||
| 1F0571400 | E6DZ3V428AARM | 4593449AA | 7B0407272A |
| 1F0571410 | E8DZ3V427AARM | 4641855AE | 7B0407272B |
| 1F2Z3B436AA | E8DZ3V428AARM | 4641855EE | 7B0407272C |
| 2F1Z3A428CA | E90Y3V427AARM | 4641856AD | R4881214AE |
| 2M5Z3B437CA | E90Y3V428AARM | 4641856AF | RL189279AA |
| 4F1Z3B437BA | F0DZ3V427AARM | 4885710AC | 557180AG |
| 5M6Z3A428AA | F0DZ3V428AARM | 4885710AE | 5170822AA |
| 5S4Z3B437AA | F21Z3B437A | 4885710AF | 52114390AA |
| 66-2005 | F21Z3B437B | 4885710AG | 5273546AD |
| 66-2008 | F2DZ3B436A | 4885711AC | 5273546AE |
| 66-2571 | F2DZ3B436B | 4885711AD | 5273546AF |
| 66-2084 | F2DZ3B437A | 4885712AC | 5273558AB |
| 66-2086 | F2DZ3B437B | 4885712AE | 5273558AD |
| 66-2095 | F4DZ3B437A | 4885712AG | 5273558AE |
| 66-2101 | F57Z3B436BA | 4885712AH | 5273558AF |
| 66-2143 | F57Z3B437BA | 4885713AC | 4881214AC |
| 6S4Z3B437BA | F5DZ3A427BA | 4885713AG | 4881214AF |
| 8S4Z3B437A | F5DZ3A428AS | 4885713AI | 4881214AG |
| 9L8Z3A427A | F5DZ3B426D | 4885713AJ | 557130AA |
| E6DZ3V427AARM | F5DZ3B436D | 5273558AG | 557180AE |
| YF1Z3A428RS | F5DZ3B437B | 66-3382 | 557180AF |
| YL8Z3A428DA | F5TZ3B436A | 66-3511 | 66-3514 |
| YS4Z3B437BB | GG032560XG | 66-3759 | 66-3564 |
| YS4Z3B437CB | GG362550X | ||
| YF1Z3A427L | |||
| for CHEVROLET | for JEEP | ||
| 257191 | 26062613 | 4578885AA | 5215710AA |
| 22791460 | 4578885AB | 5215711AB | |
| 26011961 | 4578885AC | 5215711AB | |
| 26571730 | 2657189 | 4720380 | 5273438AC |
| 2657165 | 66-1401 | 4720381 | 5273438AD |
| 26058932 | 66-1438 | 5012456AB | 5273438AE |
| 26065719 | 88982496 | 5012457AB | 5273438AG |
| for HUMMER | 5066571AA | 66-3220 | |
| 1571204 | 595716 | 557120AB | 66-3221 |
| 15886012 | 66-1417 | 557120AC | 66-3298 |
| for CADILLAC | 557120AD | 66-3352 | |
| 88957151 | 66-1416 | 557120AE | 66-3417 |
| 66-1009 | 66-1430 | 5189278AA | 66-3418 |
| 66-1415 | 88957150 | 5189279AA | 66-3419 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2024-03-15
China Custom Gjf Car CV Joint Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG Hilux Vigo Kun25 Tgn26 Kun51 43430-0K020 2004-Hot Sale Products
Product Description
Product Description
1.We are manufacturer of cv drive shaft,cv axle, cv joint and cv boot, we have more than 20-years experience in producing and selling auto parts.
2.We have strict quality control, the quality of our products is very good.
3.We are professional in different market around the world.
4.The reviews our customers given us are very positive, we have confidence in our products.
5.OEM/ODM is available, meet your requirements well.
6.Large warehouse, huge stocks!!! friendly for those customers who want some quantity.
7.Ship products out very fastly, we have stock.
| Product Name | Drive shaft | Material | 42CrMo alloy steel |
| Car fitment | Toyota | Warranty | 12 months |
| Model | for CZPT CZPT Honda CZPT CZPT CZPT VW Mazda BMW | Place of origin | ZHangZhoug, China |
| Productive year | pls contact us for more details | MOQ | 4 PCS |
| OE number | factory standard | Delivery time | 1-7 days |
| OEM/ODM | Yes | Brand | GJF |
| Packing size | according to each model | Payment | L/C,T/T,western Union,Cash,PayPal |
| Sample service | Depends on the situation of stock | Weight | 7.9KG |
Detailed Photos
Customer Review
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Axle Number: | 1 |
| Samples: |
US$ 42.8/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
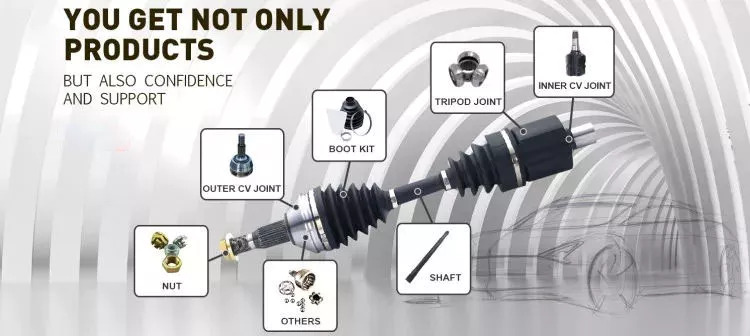
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery:
Drive shafts are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transmitting power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer:
Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability:
Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability:
Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency:
Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades:
Drive shaft upgrades can be a popular performance enhancement for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications:
Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability:
Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies:
Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency,and enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.
What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by CX 2024-03-07
China Custom Auto Parts Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG Sunny Teana Navara Pickup Car Accessories CV Axle Shaft
Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +800 items for all kinds of car, main suitable
for AMERICA & EUROPE market.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 5pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
5. Develope new items: FREE
|
Brand Name |
KOWA DRIVE SHAFT |
|
Item name |
OEM |
|
Car maker |
For all japanese/korean/european/american car |
|
Moq |
5pcs |
|
Guarantee |
12 months |
|
sample |
Available if have stock |
|
Price |
Send inquiry to get lastest price |
|
BOX/QTY |
1PCS/Bag 4PCS /CTNS |
For some items, we have stock, small order (+3000USD) is welcome.
The following items are some of drive shafts, If you need more information, pls contact us for ASAP.
| For Japanese Car | |||
| for TOYOTA | for TOYOTA | ||
| 43420-57170 | 43420-57180 | 43410-0W081 | 43420-0W080 |
| 43410-57120 | 43420-57190 | 43410-0W091 | 43420-0W090 |
| 43410-57130 | 43420-57120 | 43410-0W100 | 43420-0W110 |
| 43410-57150 | 43420-02B10 | 43410-0W110 | 43420-0W160 |
| 43410-06221 | 43420-02B11 | 43410-0W140 | 43420-32161 |
| 43410-06231 | 43420-02B60 | 43410-0W150 | 43420-33250 |
| 43410-06460 | 43420-02B61 | 43410-0W180 | 43420-33280 |
| 43410-06570 | 43420-02B62 | 43410-12410 | 43420-48090 |
| 43410-06580 | 43420-06221 | 43410-33280 | 43420-48091 |
| 43410-066-90 | 43420-06231 | 43410-33290 | 43430OK571 |
| 43410-06750 | 43420-06460 | 43410-33330 | 66-5245 |
| 43410-06780 | 43420-06490 | 43410-48070 | 66-5247 |
| 43410-06A40 | 43420-06500 | 43410-48071 | 43420-57150 |
| 43410-06A50 | 43420- 0571 0 | 43410-0W061 | 43420-0W061 |
| 43410-07070 | 43420-06610 | 43410-0W071 | 43420-0W071 |
| for Acura | for LEXUS | ||
| 44305STKA00 | 66-4198 | 43410-06200 | 43410-06480 |
| 44305STKA01 | 66-4261 | 43410-06450 | 43410-06560 |
| 44305SZPA00 | 66-4262 | 66-5265 | |
| 44306STKA00 | 66-4270 | for MITSUBISHI | |
| 44306STKA01 | 66-4271 | 3815A309 | 3815A310 |
| 44306SZPA00 | |||
| for Honda | for MAZDA | ||
| 44571S1571 | 44306S3VA61 | 5L8Z3A428AB | GG052550XD |
| 44011S1571 | 44306S3VA62 | 5L8Z3A428DA | GG052560XE |
| 44305S2HN50 | 44306S9VA51 | 66-2090 | GG362550XA |
| 44305SCVA50 | 44306S9VA71 | 6L8Z3A428A | YL8Z3A427AA |
| 44305SCVA51 | 44306SCVA50 | 9L8Z3A427B | YL8Z3A427BA |
| 44305SCVA90 | 44306SCVA51 | GG032550XD | YL8Z3A428AA |
| 44305SCVA91 | 44306SCVA90 | GG042550XD | YL8Z3A428BA |
| 44305STXA02 | 44306SCVA91 | GG042560XG | ZC32550XA |
| 44305SZAA01 | 44306STXA02 | for Nissan | |
| 44306S2H951 | 44306SZAA01 | 39101-1HS0A | 39100-1HS0A |
| 44306SZAA11 | 44306SZAA01RM | 39101-1HS0B | 39100-1HS0B |
| 44306SZAA12 | 66-4213 | ||
| 66-4214 | |||
| for Europe Car | |||
| for VOLKSWAGEN | for VOLKSWAGEN | ||
| 4885712AD | 7B0407271B | 7E0407271G | 7LA407272C |
| 4885713AF | 7B0407272 | 7E0407271P | 7LA4 0571 2CX |
| 4881214AE | 7B0407272E | 7LA407271E | |
| 7B0407271A | |||
| for America Car | |||
| for CHRYSLER | for MERCURY | ||
| 4593447AA | 557180AD | 4F1Z3B437AA | GG322560X |
| 4641855AA | 52114390AB | 5L8Z3A428DB | GG362560XA |
| 4641855AC | 5273546AC | 66-2249 | YL8Z3A427CA |
| 4641856AA | 66-3108 | 9L8Z3A427C | YL8Z3A427DA |
| 4641856AC | 66-3109 | 9L8Z3A427D | YL8Z3A427EA |
| 4882517 | 66-3130 | GG062550XD | YL8Z3A427FA |
| 4882518 | 66-3131 | GG062560XE | YL8Z3A428CA |
| 4882519 | 66-3234 | GG312560X | ZZDA2560X |
| 4882520 | 66-3518 | ZZDA2560XC | ZZDA2560XA |
| 557130AB | 66-3520 | for RAM | |
| 66-3552 | 66-3522 | 4885713AD | 55719AB |
| 66-3553 | 66-3551 | 4881214AD | 66-3404 |
| 66-3554 | 66-3639 | 55719AA | 66-3740 |
| 68193908AB | 66-3641 | 68571398AA | |
| for FORD | for DODGE | ||
| 1F0571400 | E6DZ3V428AARM | 4593449AA | 7B0407272A |
| 1F0571410 | E8DZ3V427AARM | 4641855AE | 7B0407272B |
| 1F2Z3B436AA | E8DZ3V428AARM | 4641855EE | 7B0407272C |
| 2F1Z3A428CA | E90Y3V427AARM | 4641856AD | R4881214AE |
| 2M5Z3B437CA | E90Y3V428AARM | 4641856AF | RL189279AA |
| 4F1Z3B437BA | F0DZ3V427AARM | 4885710AC | 557180AG |
| 5M6Z3A428AA | F0DZ3V428AARM | 4885710AE | 5170822AA |
| 5S4Z3B437AA | F21Z3B437A | 4885710AF | 52114390AA |
| 66-2005 | F21Z3B437B | 4885710AG | 5273546AD |
| 66-2008 | F2DZ3B436A | 4885711AC | 5273546AE |
| 66-2571 | F2DZ3B436B | 4885711AD | 5273546AF |
| 66-2084 | F2DZ3B437A | 4885712AC | 5273558AB |
| 66-2086 | F2DZ3B437B | 4885712AE | 5273558AD |
| 66-2095 | F4DZ3B437A | 4885712AG | 5273558AE |
| 66-2101 | F57Z3B436BA | 4885712AH | 5273558AF |
| 66-2143 | F57Z3B437BA | 4885713AC | 4881214AC |
| 6S4Z3B437BA | F5DZ3A427BA | 4885713AG | 4881214AF |
| 8S4Z3B437A | F5DZ3A428AS | 4885713AI | 4881214AG |
| 9L8Z3A427A | F5DZ3B426D | 4885713AJ | 557130AA |
| E6DZ3V427AARM | F5DZ3B436D | 5273558AG | 557180AE |
| YF1Z3A428RS | F5DZ3B437B | 66-3382 | 557180AF |
| YL8Z3A428DA | F5TZ3B436A | 66-3511 | 66-3514 |
| YS4Z3B437BB | GG032560XG | 66-3759 | 66-3564 |
| YS4Z3B437CB | GG362550X | ||
| YF1Z3A427L | |||
| for CHEVROLET | for JEEP | ||
| 257191 | 26062613 | 4578885AA | 5215710AA |
| 22791460 | 4578885AB | 5215711AB | |
| 26011961 | 4578885AC | 5215711AB | |
| 26571730 | 2657189 | 4720380 | 5273438AC |
| 2657165 | 66-1401 | 4720381 | 5273438AD |
| 26058932 | 66-1438 | 5012456AB | 5273438AE |
| 26065719 | 88982496 | 5012457AB | 5273438AG |
| for HUMMER | 5066571AA | 66-3220 | |
| 1571204 | 595716 | 557120AB | 66-3221 |
| 15886012 | 66-1417 | 557120AC | 66-3298 |
| for CADILLAC | 557120AD | 66-3352 | |
| 88957151 | 66-1416 | 557120AE | 66-3417 |
| 66-1009 | 66-1430 | 5189278AA | 66-3418 |
| 66-1415 | 88957150 | 5189279AA | 66-3419 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

How do drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power in various applications?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in transferring rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in various applications. Whether it’s in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission and facilitate the functioning of different systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power:
1. Vehicle Applications:
In vehicles, drive shafts are responsible for transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. The drive shaft connects the gearbox or transmission output shaft to the differential, which further distributes the power to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the drive shaft to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward. This power transfer allows the vehicle to accelerate, maintain speed, and overcome resistance, such as friction and inclines.
2. Machinery Applications:
In machinery, drive shafts are utilized to transfer rotational power from the engine or motor to various driven components. For example, in industrial machinery, drive shafts may be used to transmit power to pumps, generators, conveyors, or other mechanical systems. In agricultural machinery, drive shafts are commonly employed to connect the power source to equipment such as harvesters, balers, or irrigation systems. Drive shafts enable these machines to perform their intended functions by delivering rotational power to the necessary components.
3. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts are designed to transmit rotational power efficiently and reliably. They are capable of transferring substantial amounts of torque from the engine to the wheels or driven components. The torque generated by the engine is transmitted through the drive shaft without significant power losses. By maintaining a rigid connection between the engine and the driven components, drive shafts ensure that the power produced by the engine is effectively utilized in performing useful work.
4. Flexible Coupling:
One of the key functions of drive shafts is to provide a flexible coupling between the engine/transmission and the wheels or driven components. This flexibility allows the drive shaft to accommodate angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the engine and the driven system. In vehicles, as the suspension system moves or the wheels encounter uneven terrain, the drive shaft adjusts its length and angle to maintain a constant power transfer. This flexibility helps prevent excessive stress on the drivetrain components and ensures smooth power transmission.
5. Torque and Speed Transmission:
Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). Drive shafts must be capable of handling the torque requirements of the application without excessive twisting or bending. Additionally, they need to maintain the desired rotational speed to ensure the proper functioning of the driven components. Proper design, material selection, and balancing of the drive shafts contribute to efficient torque and speed transmission.
6. Length and Balance:
The length and balance of drive shafts are critical factors in their performance. The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven components. It should be appropriately sized to avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Drive shafts are carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can affect the overall performance, comfort, and longevity of the drivetrain system.
7. Safety and Maintenance:
Drive shafts require proper safety measures and regular maintenance. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts, reducing the risk of injury. Safety shields or guards may also be installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the drive shaft for wear, damage, or misalignment, and ensuring proper lubrication of the U-joints. These measures help prevent failures, ensure optimal performance, and extend the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, drive shafts play a vital role in transferring rotational power in various applications. Whether in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. They provide a flexible coupling, handle torque and speed transmission, accommodate angular movement, and contribute to the safety and maintenance of the system. By effectively transferring rotational power, drive shafts facilitate the functioning and performance of vehicles and machinery in numerous industries.


editor by CX 2024-02-29
China Professional CHINAMFG Car Spare Auto Parts Front CV Axle Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG CHINAMFG Honda CHINAMFG Mazda CHINAMFG Car Accessories Axle C. V. Joint
Product Description
Product Description
| Item Name | Drive shaft/ C.V Joint/ C.V Boot Cover 95% Japanese Car Model |
| Car model | For Toyota,Honda,Nissan,Mitsubishi,Mazda,Hyundai,Kia,Subaru |
| Brand | EEP |
| Qty/Box | 1 PC/Box |
| MOQ | 4PCS |
| Warranty | 1 Year/30,000-60,000Kilometers |
| Packing | EEP poly bag + CZPT color box+EEP Carton or customized packing |
| Payment | T/T, Western Union, L/C, Cash |
| Delivery | 1-7 days for stock items, 7-25 days for production order |
| Shipment | by DHL/ FEDEX/ TNT, by Air, by sea |
| Certificate | ISO9001, TS16949, SGS |
Detailed Photos
Product Specification:
| Constant velocity universal joint special steel CF53 | Normalization treatment to refine the internal structure of the material and greatly improve the performance of the C.V Joint. |
| C.V Boot | Imported neoprene to ensure of its hardness, high or low temperature test (-40 ºC –120 ºC) and high performance for elongation. |
| 1CR13 Clamp | Adopted 1CR13 martensitic stainless steel with high strength and strong corrosion resistance. |
| Molybdenum Disulfide Grease | Ample grease, operating efficiently under -40 ° C ~ 150 ° C temperature, effectively reduce metal wear by its excellent wear resistance and extend products’ service life by strong anti-aging performance. |
EEP Auto Parts CO., Ltd main products line:
1. Auto rubber bushing: engine mount, strut mount, center bearing, differential mount, control arm bushing, stabilizer bushing, other suspension bushing
2. Suspension Parts: shock absorber, control arm, ball joint,stabilizer link, tie rod end, steering rack
3. CV joint, drive shaft, cv joint boot
4. Brake parts: brake pads, brake disc, brake master cylinder, wheel cylinder
5. Fuel pump, water pump, radiator, gasket kit, engine belt
Our Advantages
Advantages of Service:
• OEM & ODM Availability
• Years of cooperation with global top brand companies
• 100% performance test before delivery
• 10000+ part numbers
• Storage sales: NO MOQ
• Punctual delivery date & shorter lead time
• Positive customer testimonials from 108 countries
• Complete products range
Certifications
Company Profile
Exhibition Show:
We attend professional auto parts trade fair to promote our products. A great many of customers would come to our booth, show interest in our products and are willing to try our products. Trial order to test quality is warmly welcomed too!
EEP Auto Parts CO., Ltd company profile:
CZPT AUTO PARTS CO., LTD, established in 1995, has been specializing in manufacturing and selling suspension parts for Japanese cars with 27 years experience. EEP AUTO PARTS has developed more than 8000 different OEM codes for Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Mitsubishi, Mazda and Subaru including shock absorber, ball joint, stabilizer link, tie rod end, rack end, control arm, bushing and mounting. We have been committed to providing high efficiency, quality guaranteed, long durability auto parts to our customers. Until now CZPT Auto Parts CO., Ltd owns 3 branch companiese which are respectively located in HangZhou, Urumchi and ZheJiang . Each branch is in charge of different markets in order to meet customers’ needs in different countries, total warehouse covering area 31,600 square meters,thus, we are able to deliver goods to you promptly.
FAQ
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Silver, Black |
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan, Toyota, Ford, Honda Mitsubishi Mazda Benz |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by CX 2024-02-15
China best CZPT Car Spare Auto Parts Front CV Axle Drive Shaft for CZPT CZPT Honda CZPT Mazda CZPT Car Accessories Axle C. V. Joint
Product Description
Product Description
| Item Name | Drive shaft/ C.V Joint/ C.V Boot Cover 95% Japanese Car Model |
| Car model | For Toyota,Honda,Nissan,Mitsubishi,Mazda,Hyundai,Kia,Subaru |
| Brand | EEP |
| Qty/Box | 1 PC/Box |
| MOQ | 4PCS |
| Warranty | 1 Year/30,000-60,000Kilometers |
| Packing | EEP poly bag + CZPT color box+EEP Carton or customized packing |
| Payment | T/T, Western Union, L/C, Cash |
| Delivery | 1-7 days for stock items, 7-25 days for production order |
| Shipment | by DHL/ FEDEX/ TNT, by Air, by sea |
| Certificate | ISO9001, TS16949, SGS |
Detailed Photos
Product Specification:
| Constant velocity universal joint special steel CF53 | Normalization treatment to refine the internal structure of the material and greatly improve the performance of the C.V Joint. |
| C.V Boot | Imported neoprene to ensure of its hardness, high or low temperature test (-40 ºC –120 ºC) and high performance for elongation. |
| 1CR13 Clamp | Adopted 1CR13 martensitic stainless steel with high strength and strong corrosion resistance. |
| Molybdenum Disulfide Grease | Ample grease, operating efficiently under -40 ° C ~ 150 ° C temperature, effectively reduce metal wear by its excellent wear resistance and extend products’ service life by strong anti-aging performance. |
EEP Auto Parts CO., Ltd main products line:
1. Auto rubber bushing: engine mount, strut mount, center bearing, differential mount, control arm bushing, stabilizer bushing, other suspension bushing
2. Suspension Parts: shock absorber, control arm, ball joint,stabilizer link, tie rod end, steering rack
3. CV joint, drive shaft, cv joint boot
4. Brake parts: brake pads, brake disc, brake master cylinder, wheel cylinder
5. Fuel pump, water pump, radiator, gasket kit, engine belt
Our Advantages
Advantages of Service:
• OEM & ODM Availability
• Years of cooperation with global top brand companies
• 100% performance test before delivery
• 10000+ part numbers
• Storage sales: NO MOQ
• Punctual delivery date & shorter lead time
• Positive customer testimonials from 108 countries
• Complete products range
Certifications
Company Profile
Exhibition Show:
We attend professional auto parts trade fair to promote our products. A great many of customers would come to our booth, show interest in our products and are willing to try our products. Trial order to test quality is warmly welcomed too!
EEP Auto Parts CO., Ltd company profile:
EEP AUTO PARTS CO., LTD, established in 1995, has been specializing in manufacturing and selling suspension parts for Japanese cars with 27 years experience. EEP AUTO PARTS has developed more than 8000 different OEM codes for Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Mitsubishi, Mazda and Subaru including shock absorber, ball joint, stabilizer link, tie rod end, rack end, control arm, bushing and mounting. We have been committed to providing high efficiency, quality guaranteed, long durability auto parts to our customers. Until now CZPT Auto Parts CO., Ltd owns 3 branch companiese which are respectively located in HangZhou, Urumchi and ZheJiang . Each branch is in charge of different markets in order to meet customers’ needs in different countries, total warehouse covering area 31,600 square meters,thus, we are able to deliver goods to you promptly.
FAQ
| After-sales Service: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Silver, Black |
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan, Toyota, Ford, Honda Mitsubishi Mazda Benz |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers employ various strategies and processes to ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a drive shaft to effectively integrate and function within a specific piece of equipment or machinery. Manufacturers take into account several factors to ensure compatibility, including dimensional requirements, torque capacity, operating conditions, and specific application needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts:
1. Application Analysis:
Manufacturers begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the intended application and equipment requirements. This analysis involves understanding the specific torque and speed demands, operating conditions (such as temperature, vibration levels, and environmental factors), and any unique characteristics or constraints of the equipment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the application, manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility.
2. Customization and Design:
Manufacturers often offer customization options to adapt drive shafts to different equipment. This customization involves tailoring the dimensions, materials, joint configurations, and other parameters to match the specific requirements of the equipment. By working closely with the equipment manufacturer or end-user, manufacturers can design drive shafts that align with the equipment’s mechanical interfaces, mounting points, available space, and other constraints. Customization ensures that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the equipment, promoting compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Torque and Power Capacity:
Drive shaft manufacturers carefully determine the torque and power capacity of their products to ensure compatibility with different equipment. They consider factors such as the maximum torque requirements of the equipment, the expected operating conditions, and the safety margins necessary to withstand transient loads. By engineering drive shafts with appropriate torque ratings and power capacities, manufacturers ensure that the shaft can handle the demands of the equipment without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
4. Material Selection:
Manufacturers choose materials for drive shafts based on the specific needs of different equipment. Factors such as torque capacity, operating temperature, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements influence material selection. Drive shafts may be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, to provide the necessary strength, durability, and performance characteristics. The selected materials ensure compatibility with the equipment’s operating conditions, load requirements, and other environmental factors.
5. Joint Configurations:
Drive shafts incorporate joint configurations, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate different equipment needs. Manufacturers select and design the appropriate joint configuration based on factors such as operating angles, misalignment tolerances, and the desired level of smooth power transmission. The choice of joint configuration ensures that the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and accommodate the range of motion required by the equipment, promoting compatibility and reliable operation.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control processes and testing procedures to verify the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. These processes involve conducting dimensional inspections, material testing, torque and stress analysis, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions. By subjecting drive shafts to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria, guaranteeing compatibility with the intended equipment.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Manufacturers ensure that their drive shafts comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, provides assurance of quality, safety, and compatibility. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers meet the expectations and requirements of equipment manufacturers and end-users, ensuring that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into different equipment.
8. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft design and manufacturing processes. This collaborative approach ensures that the drive shafts are compatible with the intended equipment and meet the expectations of the end-users. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can continuously improve their products’ compatibility and performance.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment through a combination of application analysis, customization, torque and power capacity considerations, material selection, joint configurations, quality control and testing, compliance with standards, and collaboration with equipment manufacturers and end-users. These efforts enable manufacturers to design and produce drive shafts that seamlessly integrate with various equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility in different applications.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

How do drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power in various applications?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in transferring rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in various applications. Whether it’s in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission and facilitate the functioning of different systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power:
1. Vehicle Applications:
In vehicles, drive shafts are responsible for transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. The drive shaft connects the gearbox or transmission output shaft to the differential, which further distributes the power to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the drive shaft to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward. This power transfer allows the vehicle to accelerate, maintain speed, and overcome resistance, such as friction and inclines.
2. Machinery Applications:
In machinery, drive shafts are utilized to transfer rotational power from the engine or motor to various driven components. For example, in industrial machinery, drive shafts may be used to transmit power to pumps, generators, conveyors, or other mechanical systems. In agricultural machinery, drive shafts are commonly employed to connect the power source to equipment such as harvesters, balers, or irrigation systems. Drive shafts enable these machines to perform their intended functions by delivering rotational power to the necessary components.
3. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts are designed to transmit rotational power efficiently and reliably. They are capable of transferring substantial amounts of torque from the engine to the wheels or driven components. The torque generated by the engine is transmitted through the drive shaft without significant power losses. By maintaining a rigid connection between the engine and the driven components, drive shafts ensure that the power produced by the engine is effectively utilized in performing useful work.
4. Flexible Coupling:
One of the key functions of drive shafts is to provide a flexible coupling between the engine/transmission and the wheels or driven components. This flexibility allows the drive shaft to accommodate angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the engine and the driven system. In vehicles, as the suspension system moves or the wheels encounter uneven terrain, the drive shaft adjusts its length and angle to maintain a constant power transfer. This flexibility helps prevent excessive stress on the drivetrain components and ensures smooth power transmission.
5. Torque and Speed Transmission:
Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). Drive shafts must be capable of handling the torque requirements of the application without excessive twisting or bending. Additionally, they need to maintain the desired rotational speed to ensure the proper functioning of the driven components. Proper design, material selection, and balancing of the drive shafts contribute to efficient torque and speed transmission.
6. Length and Balance:
The length and balance of drive shafts are critical factors in their performance. The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven components. It should be appropriately sized to avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Drive shafts are carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can affect the overall performance, comfort, and longevity of the drivetrain system.
7. Safety and Maintenance:
Drive shafts require proper safety measures and regular maintenance. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts, reducing the risk of injury. Safety shields or guards may also be installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the drive shaft for wear, damage, or misalignment, and ensuring proper lubrication of the U-joints. These measures help prevent failures, ensure optimal performance, and extend the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, drive shafts play a vital role in transferring rotational power in various applications. Whether in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. They provide a flexible coupling, handle torque and speed transmission, accommodate angular movement, and contribute to the safety and maintenance of the system. By effectively transferring rotational power, drive shafts facilitate the functioning and performance of vehicles and machinery in numerous industries.


editor by CX 2023-09-30
China Good quality Car Auto Spare Parts Front Rear CV Axle Drive Shaft for CZPT CZPT Honda CZPT Mazda CZPT CZPT CZPT Land Rover Jeep
Product Description
Product Description
| Product Name | Car Auto Spare Parts Front Rear CV Axle Drive Shaft for CZPT CZPT Honda CZPT Mazda CZPT CZPT CZPT Land Rover Jeep |
| OEM NO. | According to Clients’ Needs |
| Car Model | For Japanese Cars |
| Gross Weight [kg] | OEM Standard |
| Number of Ribs | OEM Standard |
| Voltage [V] | OEM Standard |
| Alternator Charge Current [A] | OEM Standard |
| Color | Same as pictrue |
| Material | Plastic+Metal |
| Warranty | 1 Year |
| MOQ | 1PC if we have stock, 50PCS for production. |
| Delivery Time | 7-45 days |
| Our Advantage | 1. Advanced design and skilled workmanship gurantee the standard of our products;
2. High-quality raw materials gurantee the good performance of our products; 3.Experienced teams and mangement gurantee the production efficiency and the delivery time; 4.Our good service bring you pleasant purchase. 5. The same length as original one. 6. Lower MOQ is acceptable with more models. 7.Laser Mark for free. 8.Pallet with Film for free. |
Detailed Photos
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | 100% Brand New |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
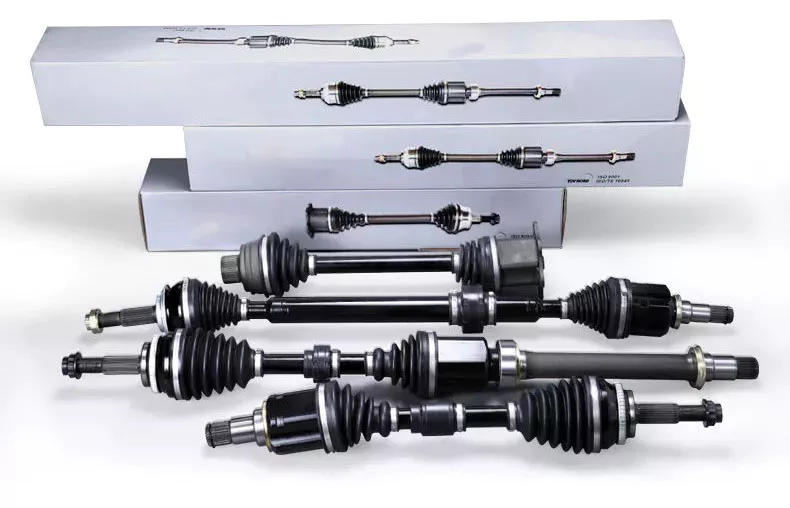

What maintenance practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts?
To prolong the lifespan of drive shafts and ensure their optimal performance, several maintenance practices are crucial. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reduces wear and tear, and ensures the drive shaft operates smoothly and efficiently. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is vital for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the drive shaft visually, looking for cracks, dents, or any signs of excessive wear on the shaft itself and its associated components such as joints, yokes, and splines. Check for any signs of lubrication leaks or contamination. Additionally, inspect the fasteners and mounting points to ensure they are secure. Early detection of any issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of drive shafts. Lubricate the joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity joints, as recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Use the appropriate lubricant specified for the specific drive shaft and application, considering factors such as temperature, load, and operating conditions. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replenish as necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Maintaining proper balancing and alignment is crucial for the lifespan of drive shafts. Imbalances or misalignments can lead to vibrations, accelerated wear, and potential failure. If vibrations or unusual noises are detected during operation, it is important to address them promptly. Perform balancing procedures as necessary, including dynamic balancing, to ensure even weight distribution along the drive shaft. Additionally, verify that the drive shaft is correctly aligned with the engine or power source and the driven components. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the drive shaft, leading to premature failure.
4. Protective Coatings:
Applying protective coatings can help prolong the lifespan of drive shafts, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Consider using coatings such as zinc plating, powder coating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance the drive shaft’s resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical damage. Regularly inspect the coating for any signs of degradation or damage, and reapply or repair as necessary to maintain the protective barrier.
5. Torque and Fastener Checks:
Ensure that the drive shaft’s fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, or clamps, are properly torqued and secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to excessive vibrations, misalignment, or even detachment of the drive shaft. Periodically check and retighten the fasteners as recommended or after any maintenance or repair procedures. Additionally, monitor the torque levels during operation to ensure they remain within the specified range, as excessive torque can strain the drive shaft and lead to premature failure.
6. Environmental Protection:
Protecting the drive shaft from environmental factors can significantly extend its lifespan. In applications exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or abrasive substances, take appropriate measures to shield the drive shaft. This may include using protective covers, seals, or guards to prevent contaminants from entering and causing damage. Regular cleaning of the drive shaft, especially in dirty or corrosive environments, can also help remove debris and prevent buildup that could compromise its performance and longevity.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to the drive shaft model and application. The manufacturer’s instructions may include specific intervals for inspections, lubrication, balancing, or other maintenance tasks. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the drive shaft is properly maintained and serviced, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
By implementing these maintenance practices, drive shafts can operate reliably, maintain efficient power transmission, and have an extended service life, ultimately reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by CX 2023-09-18
China 200cc ATV Farm Quad Bike ATVs &UTVs Buggy Car 4×4 Trike differential drive shaft
Greatest Torque(Nm): forty-60Nm
Wheelbase: 1 Engine Variable Valve Timing Sprocket For 13-sixteen Cadillac ATS Often closing Inspection just before shipment3.what can you get from us?eletric motorbike,electrical tricycle,electric moped,electrical scooter,electric vehicle4. why must you get from us not from other suppliers?we have 26 several years knowledge in electric powered automobile sector.we give top quality product and expert provider to buyer .one cooperation chance , lifelong services. 1 communication opportunity, we would be lifelong pals.5. what solutions can we give?Approved Shipping and delivery Terms: FOB,CFR,CIF,EXW, Wholesale Bicycle Crankset 170mm 104bcd Crankset Mtb Street Bicycle 89101112 Speed DDP,DDU,Categorical Delivery;Accepted Payment Currency:USD,EUR,CNYAccepted Payment Type: T/T,L/C,PayPal,Western UnionLanguage Spoken:English, China factory air compressor tiny compressor with the heart to do good high quality Chinese,Spanish

hollow drive shaft
Hollow driveshafts have many benefits. They are light and reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The largest manufacturer of these components in the world is CZPT. They also offer lightweight solutions for various applications, such as high-performance axles. CZPT driveshafts are manufactured using state-of-the-art technology. They offer excellent quality at competitive prices.
The inner diameter of the hollow shaft reduces the magnitude of the internal forces, thereby reducing the amount of torque transmitted. Unlike solid shafts, hollow shafts are getting stronger. The material inside the hollow shaft is slightly lighter, which further reduces its weight and overall torque. However, this also increases its drag at high speeds. This means that in many applications hollow driveshafts are not as efficient as solid driveshafts.
A conventional hollow drive shaft consists of a first rod 14 and a second rod 14 on both sides. The first rod is connected with the second rod, and the second rod extends in the rotation direction. The two rods are then friction welded to the central area of the hollow shaft. The frictional heat generated during the relative rotation helps to connect the two parts. Hollow drive shafts can be used in internal combustion engines and environmentally-friendly vehicles.
The main advantage of a hollow driveshaft is weight reduction. The splines of the hollow drive shaft can be designed to be smaller than the outside diameter of the hollow shaft, which can significantly reduce weight. Hollow shafts are also less likely to jam compared to solid shafts. Hollow driveshafts are expected to eventually occupy the world market for automotive driveshafts. Its advantages include fuel efficiency and greater flexibility compared to solid prop shafts.
Cardan shaft
Cardan shafts are a popular choice in industrial machinery. They are used to transmit power from one machine to another and are available in a variety of sizes and shapes. They are available in a variety of materials, including steel, copper, and aluminum. If you plan to install one of these shafts, it is important to know the different types of Cardan shafts available. To find the best option, browse the catalog.
Telescopic or “Cardan” prop shafts, also known as U-joints, are ideal for efficient torque transfer between the drive and output system. They are efficient, lightweight, and energy-efficient. They employ advanced methods, including finite element modeling (FEM), to ensure maximum performance, weight, and efficiency. Additionally, the Cardan shaft has an adjustable length for easy repositioning.
Another popular choice for driveshafts is the Cardan shaft, also known as a driveshaft. The purpose of the driveshaft is to transfer torque from the engine to the wheels. They are typically used in high-performance car engines. Some types are made of brass, iron, or steel and have unique surface designs. Cardan shafts are available in inclined and parallel configurations.
Single Cardan shafts are a common replacement for standard Cardan shafts, but if you are looking for dual Cardan shafts for your vehicle, you will want to choose the 1310 series. This type is great for lifted jeeps and requires a CV-compatible transfer case. Some even require axle spacers. The dual Cardan shafts are also designed for lifts, which means it’s a good choice for raising and lowering jeeps.
universal joint
Cardan joints are a good choice for drive shafts when operating at a constant speed. Their design allows a constant angular velocity ratio between the input and output shafts. Depending on the application, the recommended speed limit may vary depending on the operating angle, transmission power, and application. These recommendations must be based on pressure. The maximum permissible speed of the drive shaft is determined by determining the angular acceleration.
Because gimbal joints don’t require grease, they can last a long time but eventually fail. If they are poorly lubricated or dry, they can cause metal-to-metal contact. The same is true for U-joints that do not have oil filling capability. While they have a long lifespan, it can be difficult to spot warning signs that could indicate impending joint failure. To avoid this, check the drive shaft regularly.
U-joints should not exceed seventy percent of their lateral critical velocity. However, if this speed is exceeded, the part will experience unacceptable vibration, reducing its useful life. To determine the best U-joint for your application, please contact your universal joint supplier. Typically, lower speeds do not require balancing. In these cases, you should consider using a larger pitch diameter to reduce axial force.
To minimize the angular velocity and torque of the output shaft, the two joints must be in phase. Therefore, the output shaft angular displacement does not completely follow the input shaft. Instead, it will lead or lag. Figure 3 illustrates the angular velocity variation and peak displacement lead of the gimbal. The ratios are shown below. The correct torque for this application is 1360 in-Ibs.
Refurbished drive shaft
Refurbished driveshafts are a good choice for a number of reasons. They are cheaper than brand new alternatives and generally just as reliable. Driveshafts are essential to the function of any car, truck, or bus. These parts are made of hollow metal tubes. While this helps reduce weight and expense, it is vulnerable to external influences. If this happens, it may crack or bend. If the shaft suffers this type of damage, it can cause serious damage to the transmission.
A car’s driveshaft is a critical component that transmits torque from the engine to the wheels. A1 Drive Shaft is a global supplier of automotive driveshafts and related components. Their factory has the capability to refurbish and repair almost any make or model of driveshafts. Refurbished driveshafts are available for every make and model of vehicle. They can be found on the market for a variety of vehicles, including passenger cars, trucks, vans, and SUVs.
Unusual noises indicate that your driveshaft needs to be replaced. Worn U-joints and bushings can cause excessive vibration. These components cause wear on other parts of the drivetrain. If you notice any of these symptoms, please take your vehicle to the AAMCO Bay Area Center for a thorough inspection. If you suspect damage to the driveshaft, don’t wait another minute – it can be very dangerous.
The cost of replacing the drive shaft
The cost of replacing a driveshaft varies, but on average, this repair costs between $200 and $1,500. While this price may vary by vehicle, the cost of parts and labor is generally equal. If you do the repair yourself, you should know how much the parts and labor will cost before you start work. Some parts can be more expensive than others, so it’s a good idea to compare the cost of several locations before deciding where to go.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should seek a repair shop immediately. If you are still not sure if the driveshaft is damaged, do not drive the car any distance until it is repaired. Symptoms to look for include lack of power, difficulty moving the car, squeaking, clanking, or vibrating when the vehicle is moving.
Parts used in drive shafts include center support bearings, slip joints, and U-joints. The price of the driveshaft varies by vehicle and may vary by model of the same year. Also, different types of driveshafts require different repair methods and are much more expensive. Overall, though, a driveshaft replacement costs between $300 and $1,300. The process may take about an hour, depending on the vehicle model.
Several factors can lead to the need to replace the drive shaft, including bearing corrosion, damaged seals, or other components. In some cases, the U-joint indicates that the drive shaft needs to be replaced. Even if the bearings and u-joints are in good condition, they will eventually break and require the replacement of the drive shaft. However, these parts are not cheap, and if a damaged driveshaft is a symptom of a bigger problem, you should take the time to replace the shaft.


editor by Cx 2023-07-03
China 1102-2215056 Latest Design Promotional C.V.Joint Front Lada Car Drive Shaft drive shaft bearing
Error:获取返回内容失败,
Your session has expired. Please reauthenticate.

How to Identify a Faulty Drive Shaft
The most common problems associated with automotive driveshafts include clicking and rubbing noises. While driving, the noise from the driver’s seat is often noticeable. An experienced auto mechanic can easily identify whether the sound is coming from both sides or from one side. If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to send your car in for a proper diagnosis. Here’s a guide to determining if your car’s driveshaft is faulty:
Symptoms of Driveshaft Failure
If you’re having trouble turning your car, it’s time to check your vehicle’s driveshaft. A bad driveshaft can limit the overall control of your car, and you should fix it as soon as possible to avoid further problems. Other symptoms of a propshaft failure include strange noises from under the vehicle and difficulty shifting gears. Squeaking from under the vehicle is another sign of a faulty driveshaft.
If your driveshaft fails, your car will stop. Although the engine will still run, the wheels will not turn. You may hear strange noises from under the vehicle, but this is a rare symptom of a propshaft failure. However, you will have plenty of time to fix the problem. If you don’t hear any noise, the problem is not affecting your vehicle’s ability to move.
The most obvious signs of a driveshaft failure are dull sounds, squeaks or vibrations. If the drive shaft is unbalanced, it is likely to damage the transmission. It will require a trailer to remove it from your vehicle. Apart from that, it can also affect your car’s performance and require repairs. So if you hear these signs in your car, be sure to have it checked by a mechanic right away.
Drive shaft assembly
When designing a propshaft, the design should be based on the torque required to drive the vehicle. When this torque is too high, it can cause irreversible failure of the drive shaft. Therefore, a good drive shaft design should have a long service life. Here are some tips to help you design a good driveshaft. Some of the main components of the driveshaft are listed below.
Snap Ring: The snap ring is a removable part that secures the bearing cup assembly in the yoke cross hole. It also has a groove for locating the snap ring. Spline: A spline is a patented tubular machined element with a series of ridges that fit into the grooves of the mating piece. The bearing cup assembly consists of a shaft and end fittings.
U-joint: U-joint is required due to the angular displacement between the T-shaped housing and the pinion. This angle is especially large in raised 4x4s. The design of the U-joint must guarantee a constant rotational speed. Proper driveshaft design must account for the difference in angular velocity between the shafts. The T-bracket and output shaft are attached to the bearing caps at both ends.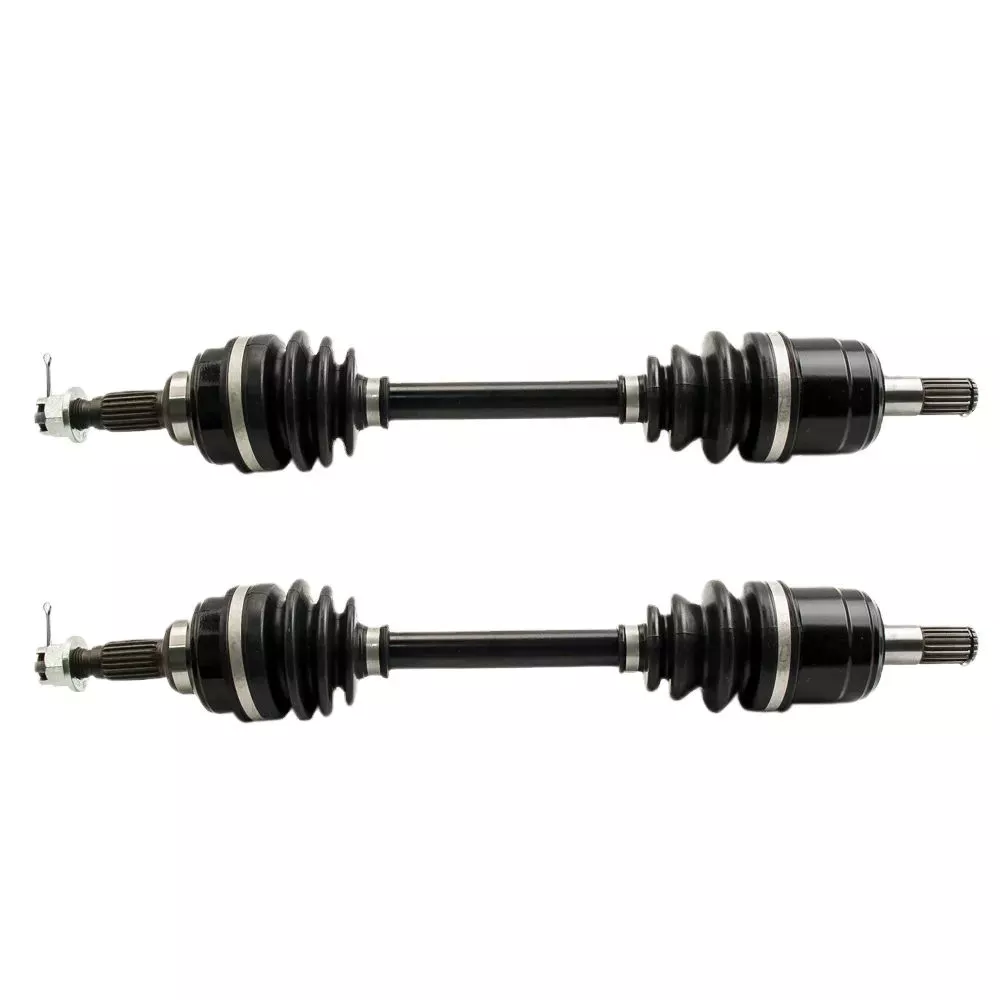
U-joint
Your vehicle has a set of U-joints on the driveshaft. If your vehicle needs to be replaced, you can do it yourself. You will need a hammer, ratchet and socket. In order to remove the U-joint, you must first remove the bearing cup. In some cases you will need to use a hammer to remove the bearing cup, you should be careful as you don’t want to damage the drive shaft. If you cannot remove the bearing cup, you can also use a vise to press it out.
There are two types of U-joints. One is held by a yoke and the other is held by a c-clamp. A full ring is safer and ideal for vehicles that are often used off-road. In some cases, a full circle can be used to repair a c-clamp u-joint.
In addition to excessive torque, extreme loads and improper lubrication are common causes of U-joint failure. The U-joint on the driveshaft can also be damaged if the engine is modified. If you are driving a vehicle with a heavily modified engine, it is not enough to replace the OE U-joint. In this case, it is important to take the time to properly lubricate these components as needed to keep them functional.
tube yoke
QU40866 Tube Yoke is a common replacement for damaged or damaged driveshaft tubes. They are desirably made of a metallic material, such as an aluminum alloy, and include a hollow portion with a lug structure at one end. Tube yokes can be manufactured using a variety of methods, including casting and forging. A common method involves drawing solid elements and machining them into the final shape. The resulting components are less expensive to produce, especially when compared to other forms.
The tube fork has a connection point to the driveshaft tube. The lug structure provides attachment points for the gimbal. Typically, the driveshaft tube is 5 inches in diameter and the lug structure is 4 inches in diameter. The lug structure also serves as a mounting point for the drive shaft. Once installed, Tube Yoke is easy to maintain. There are two types of lug structures: one is forged tube yoke and the other is welded.
Heavy-duty series drive shafts use bearing plates to secure the yoke to the U-joint. All other dimensions are secured with external snap rings. Yokes are usually machined to accept U-bolts. For some applications, grease fittings are used. This attachment is more suitable for off-road vehicles and performance vehicles.
end yoke
The end yoke of the drive shaft is an integral part of the drive train. Choosing a high-quality end yoke will help ensure long-term operation and prevent premature failure. Pat’s Driveline offers a complete line of automotive end yokes for power take-offs, differentials and auxiliary equipment. They can also measure your existing parts and provide you with high quality replacements.
A U-bolt is an industrial fastener with threaded legs. When used on a driveshaft, it provides greater stability in unstable terrain. You can purchase a U-bolt kit to secure the pinion carrier to the drive shaft. U-bolts also come with lock washers and nuts. Performance cars and off-road vehicles often use this type of attachment. But before you install it, you have to make sure the yoke is machined to accept it.
End yokes can be made of aluminum or steel and are designed to provide strength. It also offers special bolt styles for various applications. CZPT’s drivetrain is also stocked with a full line of automotive flange yokes. The company also produces custom flanged yokes for many popular brands. Since the company has a comprehensive line of replacement flange yokes, it can help you transform your drivetrain from non-serviceable to serviceable.
bushing
The first step in repairing or replacing an automotive driveshaft is to replace worn or damaged bushings. These bushings are located inside the drive shaft to provide a smooth, safe ride. The shaft rotates in a rubber sleeve. If a bushing needs to be replaced, you should first check the manual for recommendations. Some of these components may also need to be replaced, such as the clutch or swingarm.


editor by Cx 2023-06-26
China -CCL- high quality CV Axle shaft Drive Shaft DRIVE515MM For KIA CARENS AT auto transmission system car drive shaft
Product: TUCSON (JM), ix35 (LM, EL, ELH), SANTA FÉ II (CM), TUCSON (TL), COUPE (RD), CADENZA I (VG), Carnival/Grand Carnival III, SORENTO I (JC), MENTOR, Delight (DA), Rio II Stufenheck, OPIRUS, Pride Van (DA), OPTIMA, Pregio Bus, Elan, K9W4, K280A04, C90031, KI156L, 1210-IX35MTA48
Dimensions: 515MM
Content: Metal
Design Quantity: NI-8-005
Warranty: 12 Months
Automobile Make: For KIA
Other Trade Mark: PIN, EPX, CCL
Certification: ISO16949
MOQ: 4PCS
Place: Entrance Axle Still left Proper
Brand: CCL
Payment: TT Alipay Paypal Moneygram
Shipping: TNT/DHL/FEDEX
Delivery Phrase: EXW
Sample: Indeed
Automobile model: For KIA
Packaging Particulars: 1. CCL brand plastic bag, box, carton, packing belt, and woven bag2. neutral box packing
Merchandise Description
| Merchandise title: | CV JOINT FOR KIA | ||||||
| OEM Quantity: | |||||||
| Measurement: | OEM STHangZhouRD | ||||||
| Excess weight: | eight-15KG | ||||||
| Shades: | Silver,Gold,Black | ||||||
| FITTING Placement: | Inner | ||||||
| Brand name: | CCL | ||||||
| Substance: | Steel, 55 #steel | ||||||
| MOQ: | No MOQ, In accordance to Stock | ||||||
| Guarantee: | 12 Month | ||||||
| sample: | Accpet | ||||||
| Certification: | ISO 9001:2000 TS16949, SGS | ||||||
| Package: | 1PC /BOX , 4PCS /CTNS | ||||||
| Packing: | CCL Brand name Packing or as Customer’ CZPT suppliers sale NANVO oil free mute air compressor head 1.5 kw silent 50l electric powered transportable air compressors s Requirements | ||||||
| Delivery time: | 6-twenty five workdays | ||||||

How to Identify a Faulty Drive Shaft
The most common problems associated with automotive driveshafts include clicking and rubbing noises. While driving, the noise from the driver’s seat is often noticeable. An experienced auto mechanic can easily identify whether the sound is coming from both sides or from one side. If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to send your car in for a proper diagnosis. Here’s a guide to determining if your car’s driveshaft is faulty:
Symptoms of Driveshaft Failure
If you’re having trouble turning your car, it’s time to check your vehicle’s driveshaft. A bad driveshaft can limit the overall control of your car, and you should fix it as soon as possible to avoid further problems. Other symptoms of a propshaft failure include strange noises from under the vehicle and difficulty shifting gears. Squeaking from under the vehicle is another sign of a faulty driveshaft.
If your driveshaft fails, your car will stop. Although the engine will still run, the wheels will not turn. You may hear strange noises from under the vehicle, but this is a rare symptom of a propshaft failure. However, you will have plenty of time to fix the problem. If you don’t hear any noise, the problem is not affecting your vehicle’s ability to move.
The most obvious signs of a driveshaft failure are dull sounds, squeaks or vibrations. If the drive shaft is unbalanced, it is likely to damage the transmission. It will require a trailer to remove it from your vehicle. Apart from that, it can also affect your car’s performance and require repairs. So if you hear these signs in your car, be sure to have it checked by a mechanic right away.
Drive shaft assembly
When designing a propshaft, the design should be based on the torque required to drive the vehicle. When this torque is too high, it can cause irreversible failure of the drive shaft. Therefore, a good drive shaft design should have a long service life. Here are some tips to help you design a good driveshaft. Some of the main components of the driveshaft are listed below.
Snap Ring: The snap ring is a removable part that secures the bearing cup assembly in the yoke cross hole. It also has a groove for locating the snap ring. Spline: A spline is a patented tubular machined element with a series of ridges that fit into the grooves of the mating piece. The bearing cup assembly consists of a shaft and end fittings.
U-joint: U-joint is required due to the angular displacement between the T-shaped housing and the pinion. This angle is especially large in raised 4x4s. The design of the U-joint must guarantee a constant rotational speed. Proper driveshaft design must account for the difference in angular velocity between the shafts. The T-bracket and output shaft are attached to the bearing caps at both ends.
U-joint
Your vehicle has a set of U-joints on the driveshaft. If your vehicle needs to be replaced, you can do it yourself. You will need a hammer, ratchet and socket. In order to remove the U-joint, you must first remove the bearing cup. In some cases you will need to use a hammer to remove the bearing cup, you should be careful as you don’t want to damage the drive shaft. If you cannot remove the bearing cup, you can also use a vise to press it out.
There are two types of U-joints. One is held by a yoke and the other is held by a c-clamp. A full ring is safer and ideal for vehicles that are often used off-road. In some cases, a full circle can be used to repair a c-clamp u-joint.
In addition to excessive torque, extreme loads and improper lubrication are common causes of U-joint failure. The U-joint on the driveshaft can also be damaged if the engine is modified. If you are driving a vehicle with a heavily modified engine, it is not enough to replace the OE U-joint. In this case, it is important to take the time to properly lubricate these components as needed to keep them functional.
tube yoke
QU40866 Tube Yoke is a common replacement for damaged or damaged driveshaft tubes. They are desirably made of a metallic material, such as an aluminum alloy, and include a hollow portion with a lug structure at one end. Tube yokes can be manufactured using a variety of methods, including casting and forging. A common method involves drawing solid elements and machining them into the final shape. The resulting components are less expensive to produce, especially when compared to other forms.
The tube fork has a connection point to the driveshaft tube. The lug structure provides attachment points for the gimbal. Typically, the driveshaft tube is 5 inches in diameter and the lug structure is 4 inches in diameter. The lug structure also serves as a mounting point for the drive shaft. Once installed, Tube Yoke is easy to maintain. There are two types of lug structures: one is forged tube yoke and the other is welded.
Heavy-duty series drive shafts use bearing plates to secure the yoke to the U-joint. All other dimensions are secured with external snap rings. Yokes are usually machined to accept U-bolts. For some applications, grease fittings are used. This attachment is more suitable for off-road vehicles and performance vehicles.
end yoke
The end yoke of the drive shaft is an integral part of the drive train. Choosing a high-quality end yoke will help ensure long-term operation and prevent premature failure. Pat’s Driveline offers a complete line of automotive end yokes for power take-offs, differentials and auxiliary equipment. They can also measure your existing parts and provide you with high quality replacements.
A U-bolt is an industrial fastener with threaded legs. When used on a driveshaft, it provides greater stability in unstable terrain. You can purchase a U-bolt kit to secure the pinion carrier to the drive shaft. U-bolts also come with lock washers and nuts. Performance cars and off-road vehicles often use this type of attachment. But before you install it, you have to make sure the yoke is machined to accept it.
End yokes can be made of aluminum or steel and are designed to provide strength. It also offers special bolt styles for various applications. CZPT’s drivetrain is also stocked with a full line of automotive flange yokes. The company also produces custom flanged yokes for many popular brands. Since the company has a comprehensive line of replacement flange yokes, it can help you transform your drivetrain from non-serviceable to serviceable.
bushing
The first step in repairing or replacing an automotive driveshaft is to replace worn or damaged bushings. These bushings are located inside the drive shaft to provide a smooth, safe ride. The shaft rotates in a rubber sleeve. If a bushing needs to be replaced, you should first check the manual for recommendations. Some of these components may also need to be replaced, such as the clutch or swingarm.


editor by Cx 2023-06-25